EV Basics
Electric cars can travel around the same mileage as a gas powered car
Electric cars are powered on pure electricity
Electric cars are becoming more affordable and over a lifetime are cheaper than gas counterparts
Find your vehicle
With many auto manufacturers making electric vehicle models, there is an EV out there that will fit your lifestyle and driving style.
Understanding Charging
Looking at all the charging options can look a bit daunting, but it is really quite simple!
Level 1
4 to 6 miles of range per hour of charging
120 volts
1.4 to 1.9 kW
Typical 3 prong outlet
8 to 12 hours for full charge
Level 2
10 to 20 miles of range per hour of charging
240 volts
2.5 to 19.2 kW
Requires installation and cannot be transported
4 to 6 hours for full charge
Level 3
(DC Fast)
150-500 miles of range per hour of charging
480 volts<90 kW
Not available for home installation, usually found along highways and roadside
CHAdeMO or CCS chargers
Full charge in about 30 minutes
“Range Anxiety” is quickly becoming a thing of the past
With the adoption of electric cars now quickly accelerating range anxiety no longer needs to be an issue when buying an electric car! There are close to 48,000 Level 2 and DC Fast charging stations across the United States.
With bigger batteries and faster charging youll be spending more time on the roadwith the familyat the lakeseeing the mountains

How Do All-Electric Cars Work?
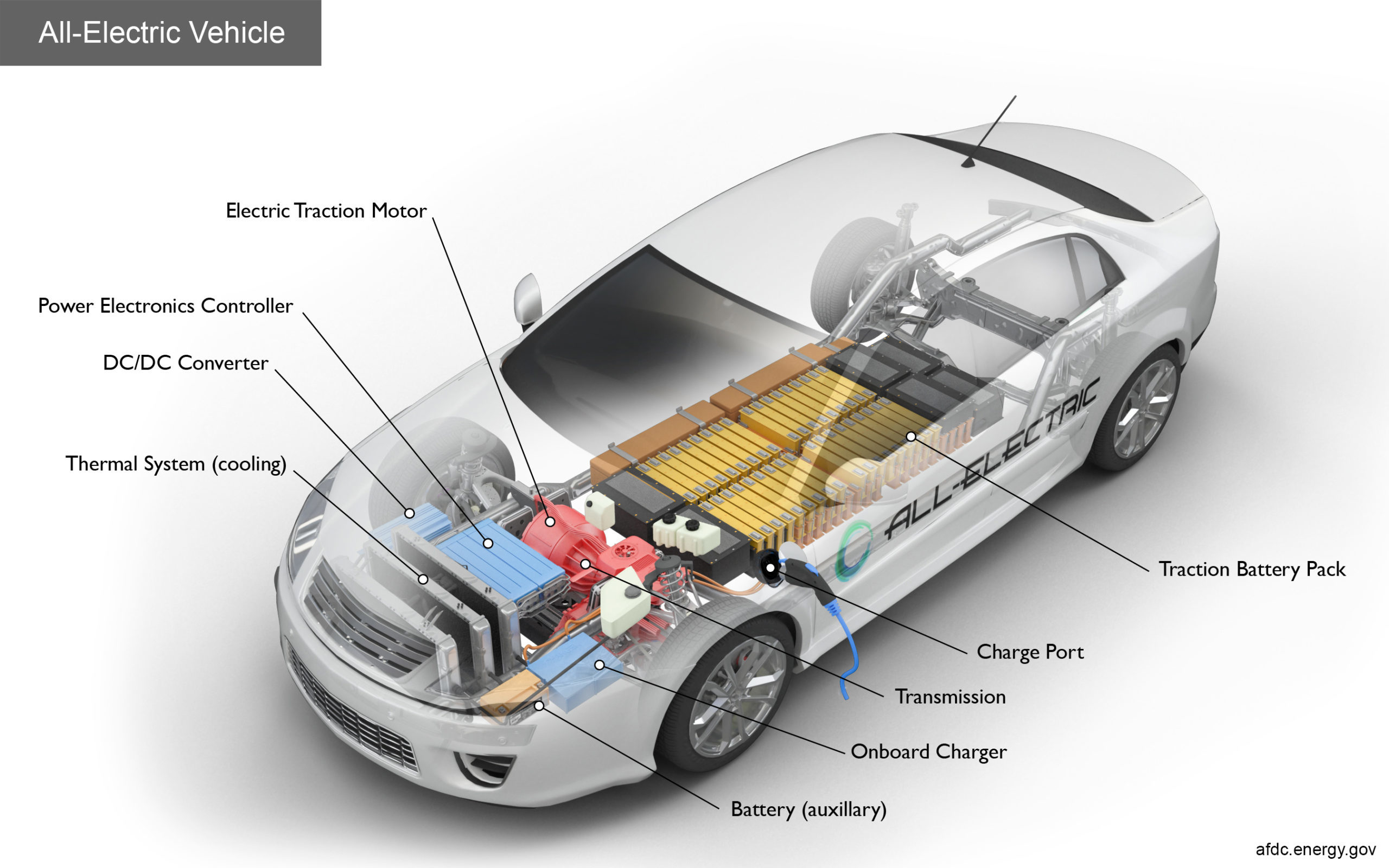
Power electronics controller: This unit manages the flow of electrical energy delivered by the traction battery, controlling the speed of the electric traction motor and the torque it produces.
Transmission (electric): The transmission transfers mechanical power from the electric traction motor to drive the wheels.
Battery (all-electric auxiliary): In an electric drive vehicle, the auxiliary battery provides electricity to power vehicle accessories.
Charge port: The charge port allows the vehicle to connect to an external power supply for charging the traction battery pack.
Thermal system (cooling): This system maintains a proper operating temperature range for the engine, electric motor, power electronics, and other components.
DC/DC converter: This device converts higher-voltage DC power from the traction battery pack to the lower-voltage DC power needed to run vehicle accessories and recharge the auxiliary battery.
Electric traction motor: Using power from the traction battery pack, this motor drives the vehicle’s wheels. Some vehicles use motor generators that perform both the drive and regeneration functions.
Onboard charger: Takes the incoming AC electricity supplied via the charge port and converts it to DC power for charging the traction battery. It also communicates with the charging equipment and monitors battery characteristics such as voltage, current, temperature, and state of charge while charging the pack.
Traction battery pack: Stores electricity for use by the electric traction motor
Other types of EVs
PHEV
PHEVs (plug-in hybrid electric vehicles) use batteries to power an electric motor, plug into the electric grid to charge, and use a petroleum-based or alternative fuel to power the internal combustion engine. Some types of PHEVs are also called extended-range electric vehicles (EREVs).
Hev
HEVs (Hybrid Electric Vehicles) are powered by an internal combustion engine in combination with one or more electric motors that use energy stored in batteries. HEVs combine the benefits of high fuel economy and low tailpipe emissions with the power and range of conventional vehicles.
Save Time
Charge your vehicle every night at home and wake up with a full battery!
Performance
Electric vehicles have instant torque and maximum power all of the time.
Emission Saving
No tailpipe means no emissions while you drive.
Other Resources
Chargepoint
The electric revolution is here.
EV Resource
A leading source of information and education about electric vehicles and the EV world.
Plug In America
We are the voice of plug-in vehicle drivers across the country.
EVgo
EV charging network that delivers fast charging to everyone.
Frequently asked questions
How long do EV batteries last?
Predictive modeling by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory indicates that today’s EV batters may last 12-15 years in moderate
climates (8-12 years in extreme climates). Several manufacturers of plug-in vehicles offer 8-year/100,000-mile battery warranties.
How far can EVs drive on a charge?
The EPA tests EVs and sets their range just like a typical gas car. Just like in a gas car, it varies by model, and can fluctuations
due to weather, driving habits, terrain, and usage. If you want to learn more about the EPA range ratings click
here!
How do EV tax credits work?
EV tax credits help defray the cost of EVs by reduce the buyers would owe that year. Tax credits amounts vary, based on the vehicle and
state, and how much you owe in taxes. The maximum federal EV tax credit is $7,500. Example: You buy a Nissan Leaf for $32,000 and
you owe $5,000 on your taxes. The maximum that you will receive will be $5,000, the extra $2,500 does not come back to you.
We suggest talking with a tax professional and check
here to see what vehicles qualify for credits.
Drive Electric Utah is run by Utah Clean Cities Coalition. Utah Clean Cities is a part of the U.S. Department of Energy Clean Cities Network, which focuses on reducing the use of fossil fuels and increasing energy independence in the United States. To learn more about Utah Clean Cities mission and work please visit UtahCleanCities.org.






